Resources Credentials to access slides:
username: nlp2019 password: 2019nlp
Notes taken by Luizo ( @LuigiBrosNin on Telegram)
Won’t be taking lessons this year, might do something if i take the exam B) (i didn’t)
1.1 Intro
Summarization of the general paradigm of Computational Linguistics
Machine Learning dominates the NLP studies
If we embrace an empiricist view, then for analyzing a specific phenomenon X in a language variety Y (both manually or with computational tools):
- we have to collect a good set of textual data (a corpus) composed of texts from the language variety Y;
- we will collect all the occurrences of the phenomenon X from the corpus;
- we will analyse the occurrences of the phenomenon X to find regularities that will allow us to completely describe the phenomenon inside the corpus;
- we will generalize our conclusions, derived from corpus analysis, to the entire variety.
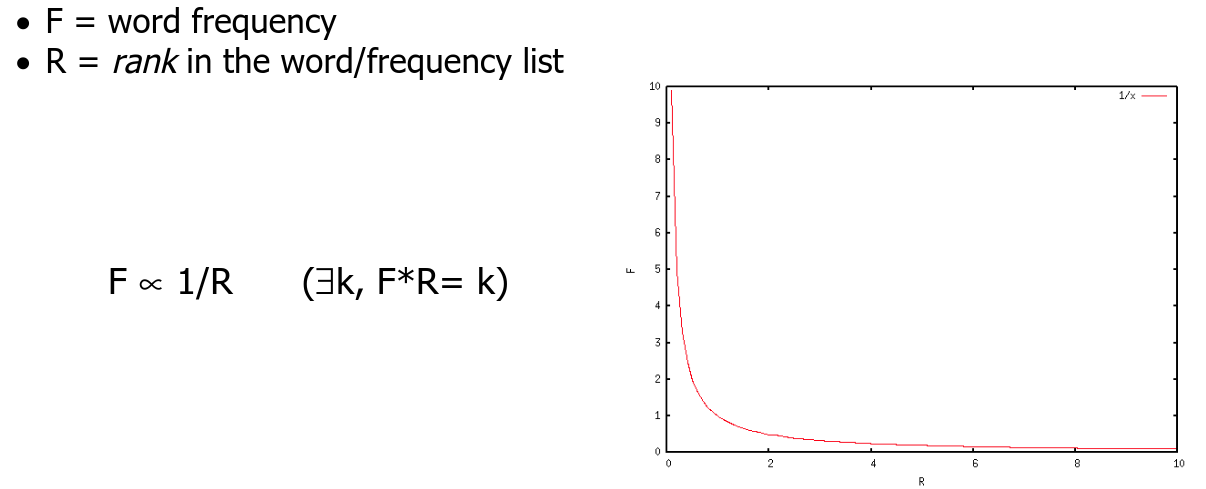
Zipf's law (1949) → a small portion of words in a language compose 40~% of each sentence
 Linguistic levels:
Linguistic levels:
- Phonetics/Phonology → how it sounds / shows for sign languages
- Morphology → the various forms words can have
- Infection (Derivations, compositions) (eg. cat/cats)
- Syntax → part of speeches, dependency, parsing, etc
- Semantics → Lexical semantics (synonymy, antonymy, etc)
- Discourse analysis / Pragmatics
- Anaphors: Mary is a woman. She loves Jhon.