🐰 i cannot fathom to remember anything about theory, i can’t explain theoretical concepts no matter how much i try to understand them, they slip my mind. I’ll try making conceptual maps to train me more to remember
1. Image Formation Process
Getting a 3D scene into a 2D image
- Geometric information
- Perspective projection
- Stereo vision
- Digitization
- Sensors for sampling (space/colour) and quantization (light)
2. Spacial Filtering
Reduce noise in images
- Concept of denoising
- Filters, compute new RGB value for each pixel
- Linear and Translation-Equivariant type of filter
- Convolution properties
- Discrete convolution → sum product of the 2 signals with 1 being reflected
- Filters
- Linear
- Mean filter
- Gaussian filter → further pixels are less important
- Non-Linear
- Median filter → middle value
- Bilateral filter → further or different pixels are less important
- Non-local Means filter → find similar patches
- Linear
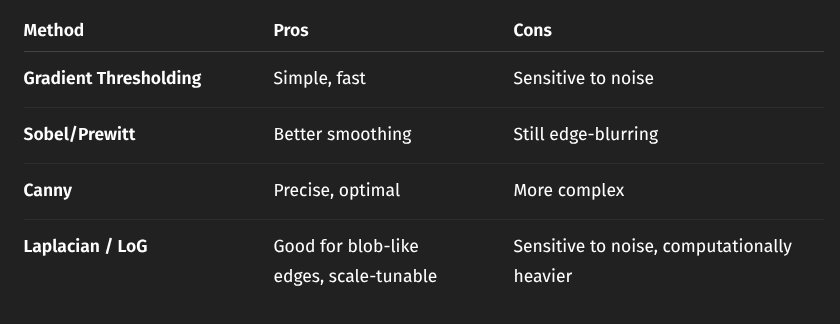
3. Edge Detection
- 1D step edge → 1st derivative
- 2D Gradient → compute partial derivatives to get direction and strength
- Discrete approximation → differences in pixels
- Noise
- Prewitt and Sobel operators → decide weights of current pixel based on brightness difference of surroundings
- Non-Maxima Suppression (NMS)
- Find local maxima along gradient
- Estimate direction locally (with Lerp from closest pixels)
- Thresholds
- Canny’s criteria
- Good detection
- Good localization
- One response, one edge
- Canny’s edge detector PIPELINE
- Gaussian smoothing
- Gradient computation
- Non-maxima suppression
- Hysteresis thresholding
- 2nd order derivative methods
- zero crossing
- Laplacian operator (sum of 2nd order derivatives) approximation
- Laplacian of Gaussian (LoG) PIPELINE
- Gaussian smoothing
- Apply Laplacian operator
- Find zero-crossings
- localize edge at sign change
- Summary
4. Local Features
find Local invariant features (corresponding points) in images
- Three-stage pipeline
- Detection
- Description
- Matching
- Properties
- Detector
- Repeatability
- Saliency
- Descriptor
- Distinctiveness vs. Robustness Trade-off → get invariant info
- Compactness
- Desirable speed for both
- Detector
- Corner detectors
- Moravec detector → look at patches and compute cornerness (high variation)
- Harris corner detector
- Compute gradients around point of interest, create matrix with results
- Compute corner score with matrix
- Threshold & NMS to pick the best corners
- Invariance properties of harry’s detector
- Rotation invariance
- Partial illumination invariance (only uniform shift)
- Scale space → concept of same img at different scales
- Linderberg (multi-scale detection)
- Use scale normalized derivatives
- Normalize filter responses
- Search extrema in 3D
- Scale-normalized LoG → filter (second order derivative) that detects blobs (circular structures)
- Difference of Gaussian (DoG) → approx of Scale-normalized LoG, find extrema across results in 3F
- Invariance of DoG
- Scale invariance
- Rotation invariance (get canonical orientation, remember local coords)
- SIFT Descriptor → Scale invariant feature transform
- take 16x16 grid around keypoint
- 4x4 subregion division
- 8-bin histogram if gradient orientations
- output vector is compact and robust
- Matching process
- Nearest neighbour search, doing it efficiently
- k-d tree
- Best Bin First
- Nearest neighbour search, doing it efficiently
5. Camera Calibration
determining a camera’s internal/external parameters to measure 3D info from 2D images
- Perspective projection
- WRF to CRF with Focal length and depth calculations
- 4th coordinate for linear perspective projection
- Digitization
- Intrinsic parameter matrix A, focal length xy, skew, central points
- Rotation matrix, Translation vector → relation CRF = R cdot WRF + T
- Homography
- simplified projection
- taken from a flat image, depth 0
- Get planar targets, estimate matrix A
- Lens distortion, Barrel / Pincushion
- Calibration estimates:
- Intrinsic parameters
- Extrinsic parameters
- Lens distortion coefficients
- Zhang’s method → computes homography
- Main Pipeline (Zhang’s method):
- Acquire images of flat pattern
- Estimate homographies
- Use to compute intrinsic matrix
- Use and to compute for each image
- Estimate lens distortion coefficients
- Use non-linear optimization to refine all parameters by minimizing reprojection error
6. CNNs
- CNN
- input image
- layers
- feature map output
- Gradient descent → how the model learns
- Optimizers
- Momentum
- RMSprop
- Adam (momentum + RMSprop)
- Convolutional layers
- Padding to keep output size
- Stride
- Deep CNNs
- Convolution + ReLU + Pooling
- Batch normalization
- Avoid vanish/explode gradients
- compute mini-batch mean and variance, adjust learnable parameters by normalization
- Regularization - prevent overfitting
- Dropout
- Early stopping
- Cutout
- Data augmentation
- modify dataset to expand it
- flip, rotate, resize, jitter
- cutout
- multi-scale training
- ResNet
7. Object Detection
Faster R-CNN → introduce Region Proposal Network, use anchors and samples
8. Segmentation
Classify area of objects 9. Evaluation metrix 1. Intersection over union 10. Segmentation masks predictions → uses fully convolutional networks for spatial maps 11. Transposed convolutions (upsampling) 12. U-Net → specialized encoder-decoder for segmentation, implements skip connections 13. Dilated convolutions - dilatate kernel to observe larger region, lose finer details - DeepLab - backbone CNN like ResNet - Remove strides and add dilation in later layers 14. Insance segmentation → classify different instances of class - Mask R-CNN, based on Faster R-CNN - Rol-Align - Bilinear interpolation for coords 15. Panoptic segmentation → get instances and general labels